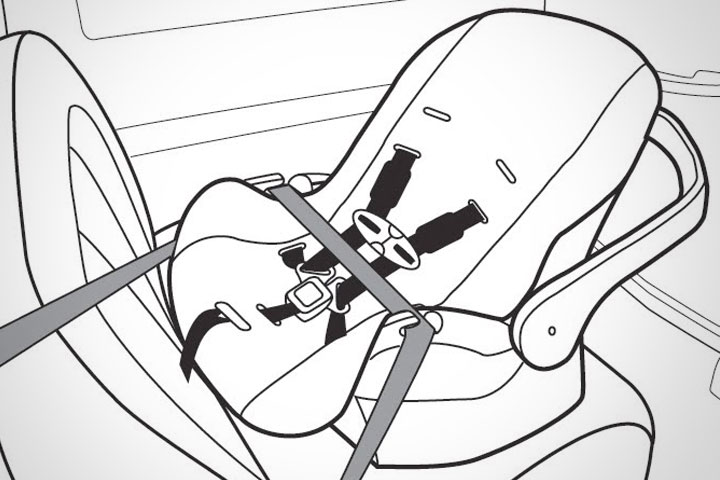
There are three types of car seats—infant seats, convertible seats, and booster seats. This guide focuses predominantly on infant and convertible seats.
- Infant Seats: Also called baby or infant carriers, infant seats are positioned facing backwards (rear-facing) in your car and are designed for infants weighing up to 20 to 22 pounds. Many infant seats come with a base that remains in the car while the seat is removable, allowing parents to take baby in and out of the car without removing her from the seat—a great feature for babies who fall asleep in the car! Remember, babies should remain rear-facing until they are at least 2 years old or have reached the maximum weight for their car seat.
- Convertible Seats: As the name implies, these seats should be positioned rear-facing until the baby reaches the maximum weight or height allowed by the maker of the car safety seat. Your child will get more use out of this seat versus an infant seat, but keep in mind the seat cannot be removed to transport a sleeping infant.
- Booster Seats: While you don't have to worry about these until your child is older, booster seats are a vital part of travel safety. They are for children who are at least 40 pounds, but are not tall enough to use only an adult seatbelt. Booster seats may be the seat only or come with a detachable back rest for extra support.